104: IBM watsonx Code Assistant
Goal
The goal of this lab is to help explore/familiarize yourself with some key capabilities available in IBM watsonx Code Assistant (WCA).
Introduction
IBM watsonx Code Assistant uses a foundation model that is managed by the IBM Research team and trained on Ansible Galaxy, GitHub, and other open sources of data.
The model offers access to Ansible content recommendations through the use of natural language automation descriptions.
The model is available through a Visual Studio Code (VS Code) extension called Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant.
How to get a recommendation from Ansible Lightspeed
-
Open or create a new workspace.
a. You can create a new workspace by selecting File > Save Workspace As...
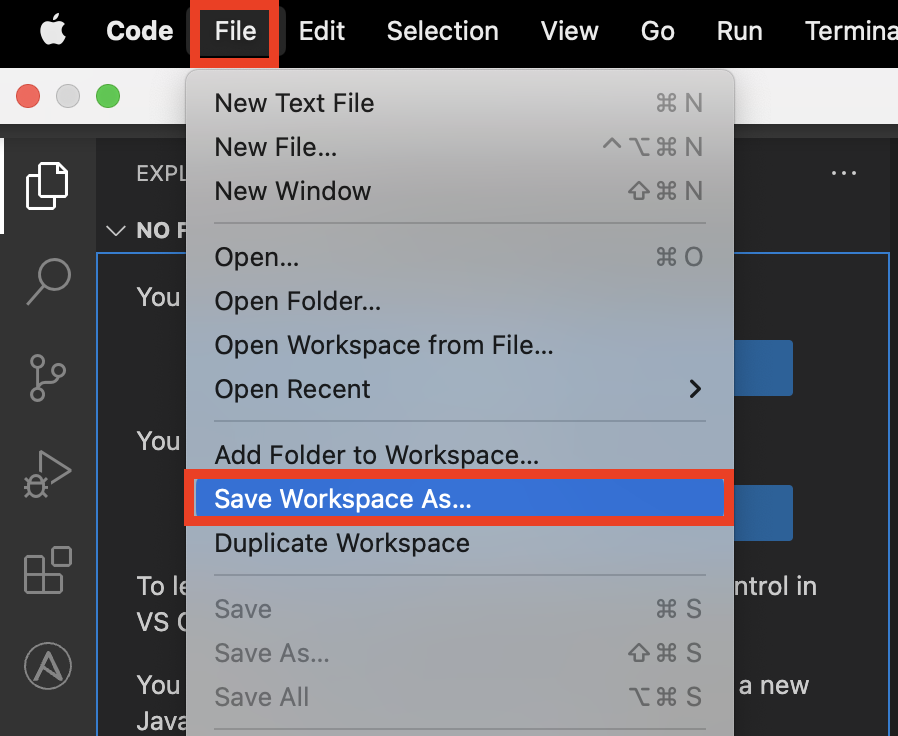
b. Name the workspace
ansible-lightspeed. Then click the Save button.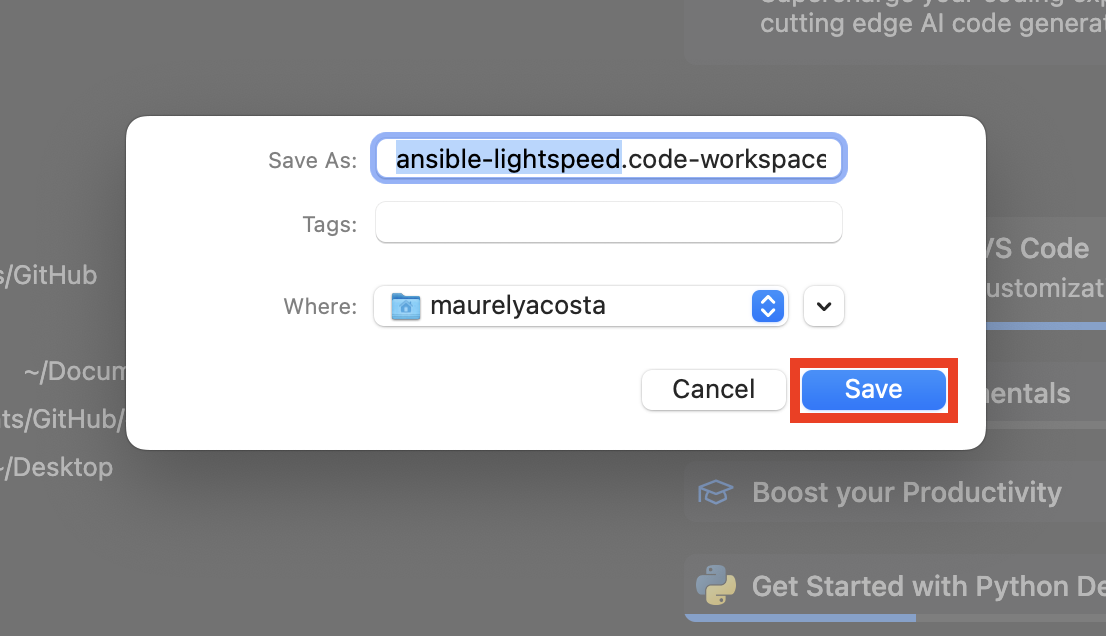
-
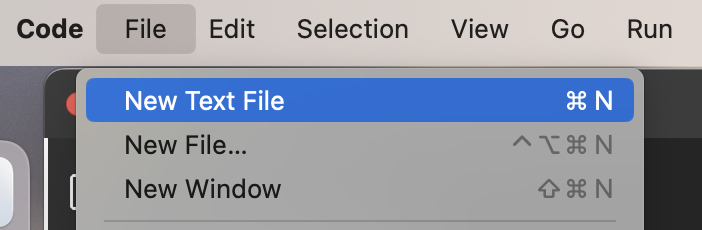
Create a new Ansible playbook by creating a new file called
lightspeed-demo.yml.a. Select File > New Text File
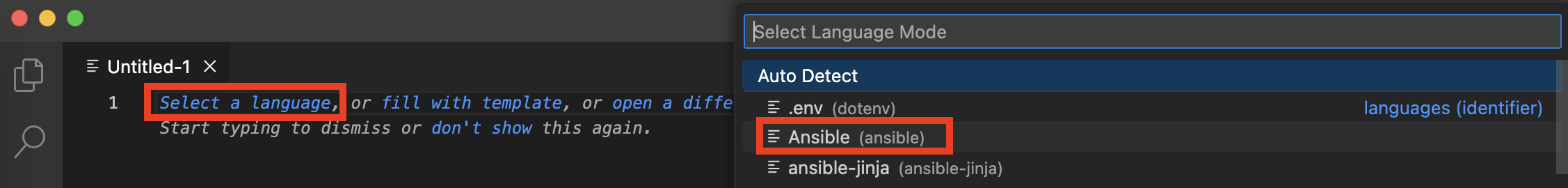
b. Click Select a language in the new file and a dropdown menu will appear then select Ansible
c. Save the file and name it
lightspeed-demowith a YAML extension (.ymlor.yaml) -
On the bottom-right corner, you should see Lightspeed. Ansible Lightspeed is ready for you to write playbooks.
Note: Check that your Python environment is also selected.

-
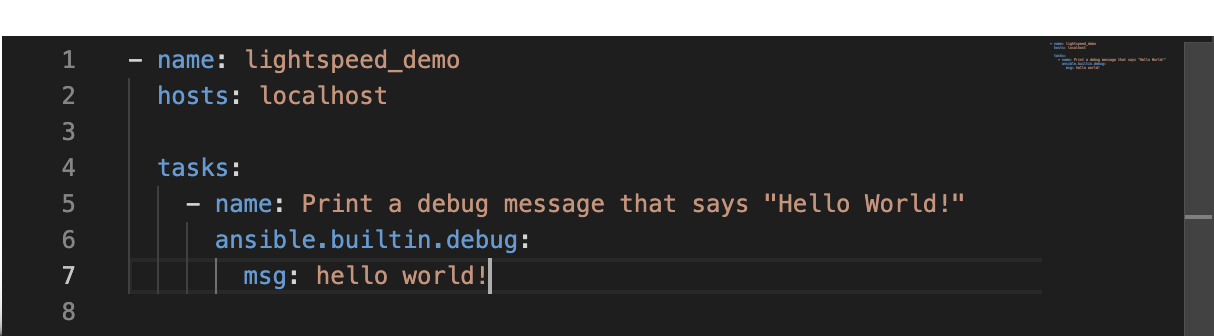
Add a new Ansible task with a name in plain English that says
Print debug message that says "Hello World!".Once you hit the Enter key, the suggestion will appear as faded text.
Lightspeed will recommend code based on the text you typed in the name field in the playbook section.

-
You can accept the recommendation by hitting the Tab key.
-
Let's add a second task to our Playbook. Write a sentence in a new
namefield that saysPrint today's date and time.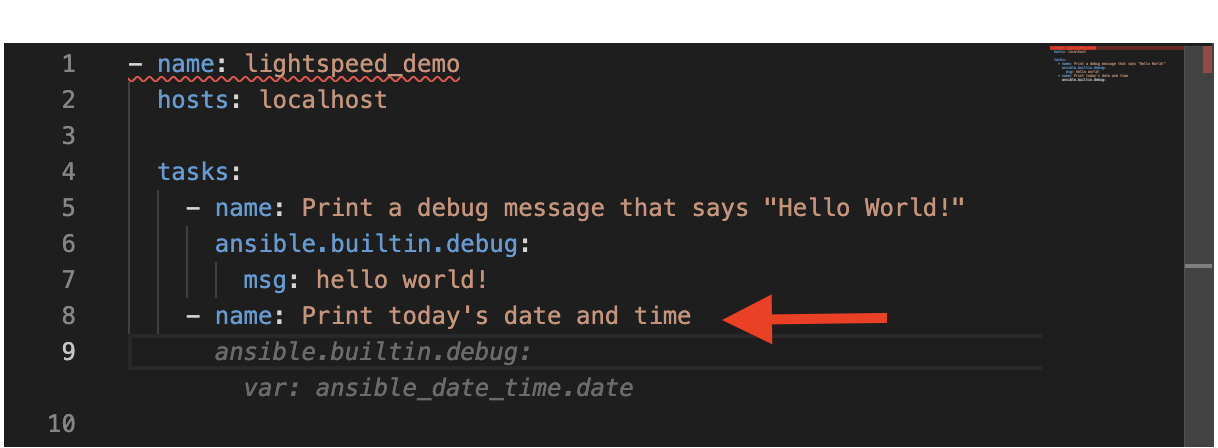
-
Press the Esc key to decline the recommendation. The faded recommendation should disappear.
-
You can see how simple it is to accept and decline a recommendation. Let's try adding a more advanced task. Create a new task with this sentence
HTTP GET request to the url https://bam-api.res.ibm.com/v1/models with bearer token with variable name bam_bearer_token.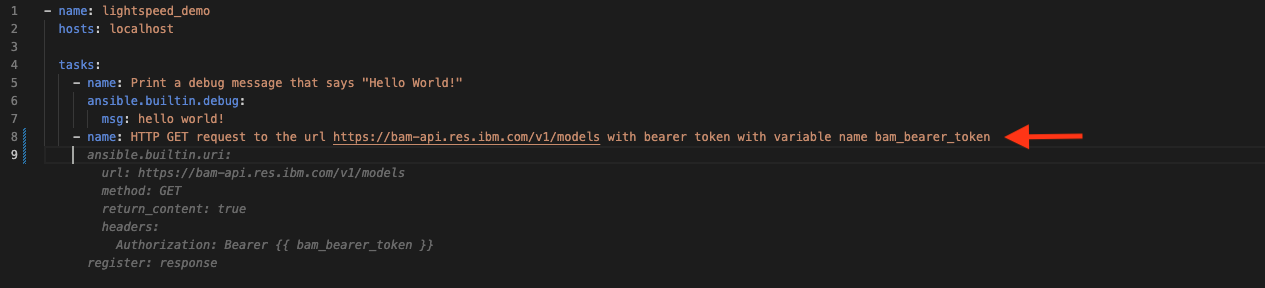
-
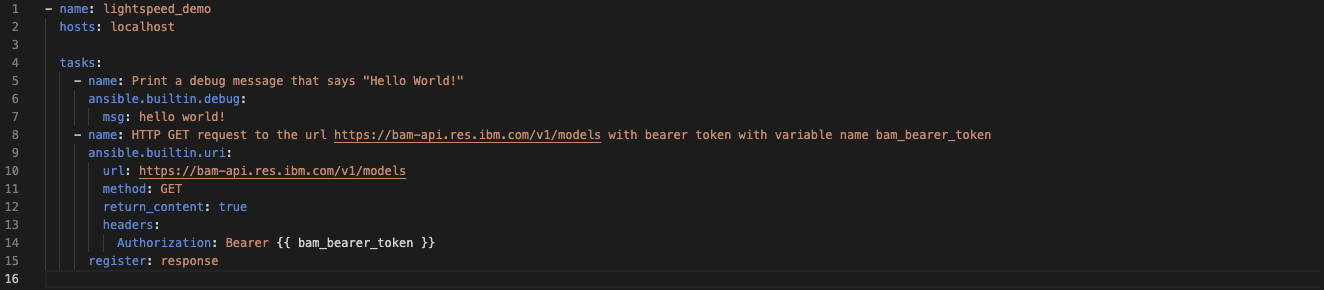
Click the Enter key and accept the recommendation by pressing the Tab key.
-
You can either copy and paste your BAM access token in place of the
{{ bam_bearer_token }}or you can retrieve your access token from your local environment and assigned it to a variable in your ansible playbook by adding the following code:vars: bam_bearer_token: "{{ lookup('env','bam_bearer_token') }}"yml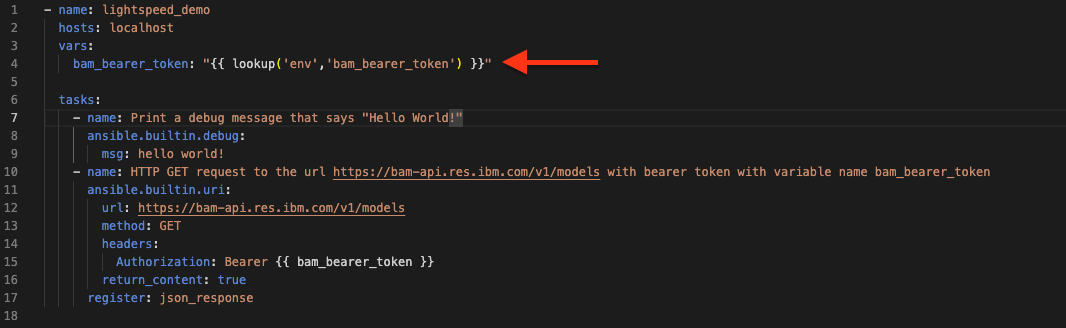
-
Add another task with the sentence
Print the result. Click the Enter key and accept the recommendation by pressing the Tab key.
Note: Lightspeed also provides source code recommendations in the debugging window beside the terminal. It shows more information if you extend it.
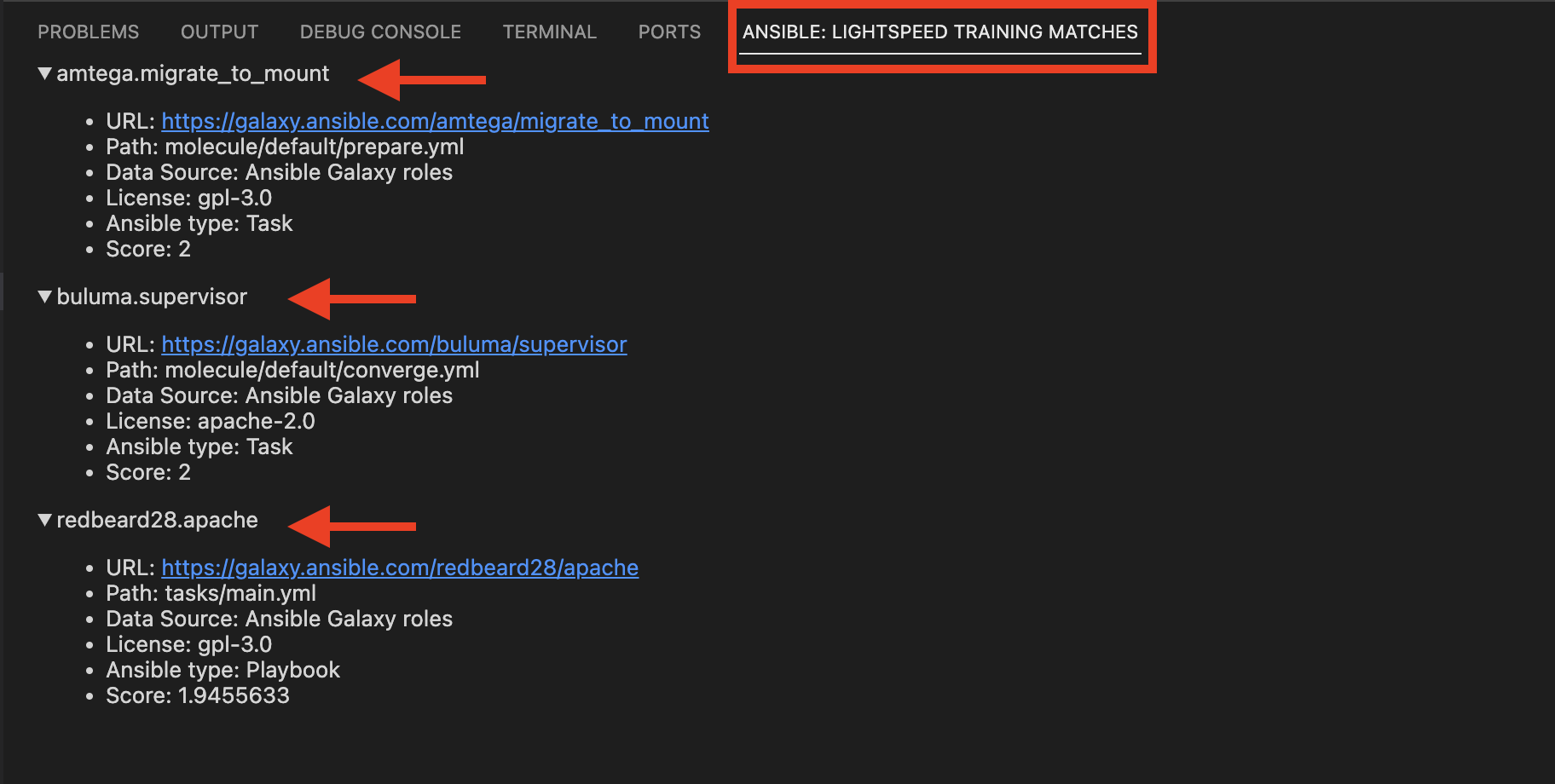
-
You can run your Ansible Playbook with the following terminal command. You should see the tasks we created being executed.
ansible-playbook lightspeed-demo.ymlbash
You can continue experimenting with creating new tasks. If you do not get a recommendation that aligns with the intent of your task name, then rephrasing your statement to provide more information on what is desired may lead to better recommendations.
The actions that you take when a recommendation is provided impact the training process of the model.
If a recommendation is accepted, and then further edits are performed, then the act of changing the recommendation to something else will be considered a modification of the recommendation. This will tell Ansible and IBM watsonx Code Assistant that the recommendation required extra editing in order to meet the intended use. This information will be used for context in training the model for similar prompts in the future.