Relevant open source technologies
PrestoDB
-
Open Source, distributed SQL query engine, designed for fast analytics queries against data of any size
-
Queries on data where it lives using ANSI SQL across federated and diverse sources
-
Supports both relational and non-relational sources
-
Also supports open source file types (ORC, Parquet, Avro, RCFile, SequenceFile, JSON, Text, CSV)
-
Excellent for connecting business intelligence tools to various data sources
-
Uses an architecture similar to classic massively parallel processing database management systems
-
One coordinator node working in sync with multiple worker nodes
-
Query gets submitted to the coordinator which uses presto’s custom query and execution engine to parse, plan, and schedule a distributed query plan across the worker nodes
-
Designed to support standard ANSI SQL semantics, including complex queries, aggregation, joins, left/right joins, subqueries, window functions, distinct counts, and approximate percentiles
Hive Metastore
Central storage point for all the meta-information about your data storages
-
Central repository for lakehouse query engines
-
Stores metadata information about connected tables, views, partitions, columns, and their respective schemas
-
Stores information such as the schema of tables, their column names, types, and partitioning information
• This information is used by the query engines to optimize query execution and improve performance
• Tracks the location of data stored in the storage systems, making it easier for the query engine to access and process the data
• Typically implemented as a relational database, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle
• Handles concurrent access and provides high availability and fault tolerance
File Formats

Open Source Table Formats
- Separation of compute, data, and storage
- Leverage low-cost, infinitely scalable object storage
- Standardized
• open file formats (Parquet, ORC, DWRF, JSON, …)
• table formats (Apache Iceberg, LF Delta, Apache Hudi)
- Accessed by scalable compute engines of choice (Presto, Spark, etc.)

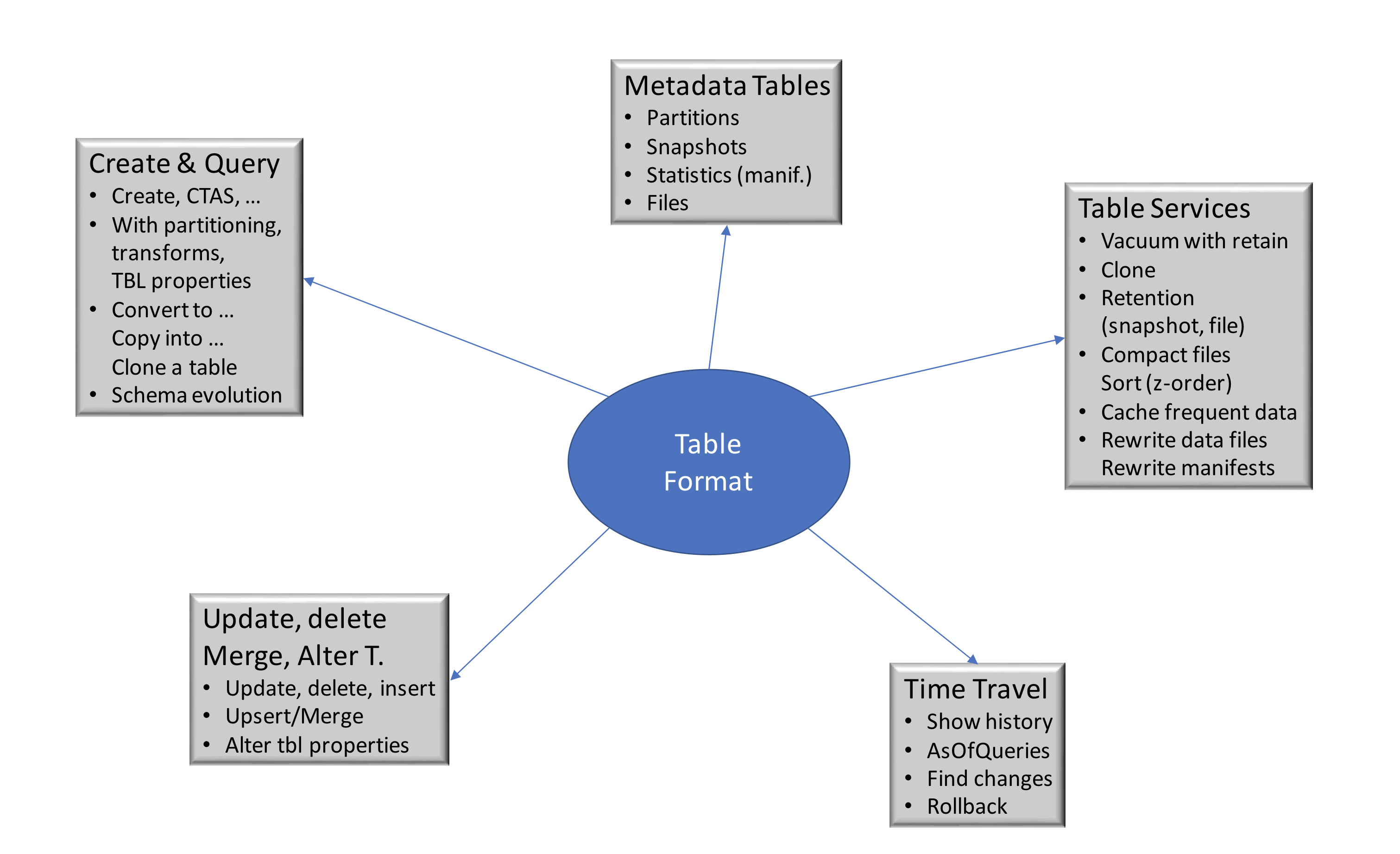
ICEBERG
Open table format for huge analytic datasets
-
Schema Evolution supports add, drop, update, or rename, and has no side-effects
-
Hidden partitioning prevents user mistakes that cause silently incorrect results or extremely slow queries
-
Partition layout evolution can update the layout of a table as data volume or query patterns change
-
Time travel enables reproducible queries that use exactly the same table snapshot, or lets users easily examine changes
-
Version rollback allows users to quickly correct problems by resetting tables to a good state
-
Advanced filtering data files are pruned with partition and column-level stats, using table metadata
• Originally designed to solve correctness problems in eventually-consistent cloud object stores
-
Works with any cloud store and reduces NN congestion when in HDFS, by avoiding listing and renames
-
Serializable isolation table changes are atomic and readers never see partial or uncommitted changes
-
Multiple concurrent writers use optimistic concurrency and will retry to ensure that compatible updates succeed, even when writes conflict