Key Data Terms
-
Data warehouse Centralized repository that stores large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from various sources within an organization. It is designed to support business intelligence (BI) activities, including reporting, analysis, and decision-making.
-
Data Mart Subset or a specialized version of a data warehouse that focuses on a specific department, function, or subject area within an organization. It contains a curated and tailored collection of data that is relevant to a particular group of users.
-
Data Lake Storage architecture that allows organizations to store large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in its raw format. It is a central repository that holds diverse data types and formats without the need for upfront data transformation or schema definition.
-
Data Lakehouse Data lakehouses are designed to be one place for all workloads, providing support for reporting, data science, AI, and machine learning on the same data, at the same time, all in one place.
-
Data Pipeline Series of processes and steps that extract, transform, and load (ETL) data from various sources into a target destination for storage, analysis, or consumption. It is a structured flow of data that ensures the reliable and efficient movement of data throughout the stages of the pipeline.
-
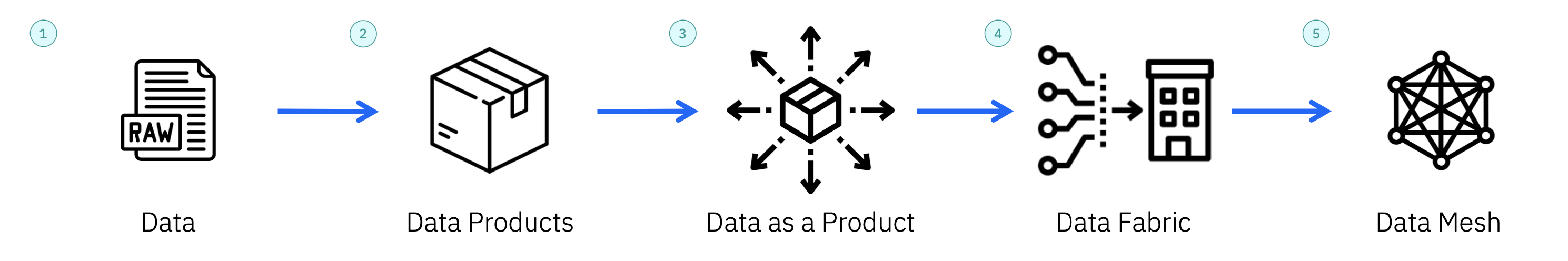
1. Data It represents the initial, untouched form of information that hasn't undergone any transformation, analysis, or interpretation and commonly associated with data lakes. It forms the basis for data analysis and is typically refined and organized into a more accessible format within a data warehouse.
-
2. Data Products A complete data package that contains three main parts
• Processed Dataset: The organized and analyzed data that provides answers or insights.
• Metadata: Data description that explains where the data comes from, how it's structured, and otherimportant details.
• Data Access Pattern: Shows how people can use or get the data, like through apps, reports, or other tools.
-
3. Data as a Product
• An operational approach of packaging data in a way that makes it easier to consume.
• The domains should consider analytical data as a first-class product rather than considering it a by-product of their business operations. They should also apply all the aspects of product development to make it valuable, useful, reliable, and customer-focused.
• Transform raw data into a valuable, accessible resource that provides useful information or insights to data consumers.
-
4. Data Fabric
• An architectural approach of simplifying data access in an organization and facilitates self-service data consumption. This architecture is agnostic to data environments, processes, utility and geography, all while integrating end-to-end data-management capabilities.
• A data fabric automates data discovery, governance, and consumption, enabling enterprises to use data to maximize their value chain by providing the right data, at the right time, regardless of where it resides.
-
Key elements of generic data fabric
-
Data ingestion
-
Data discovery
-
Data processing
-
Data access
-
Data orchestration
-
Data management & intelligence
-
-
5. Data Mesh
• An organizational approach of managing and distributing data within a company where the responsibility for data is decentralized, to treat data as a product and shift ownership and accountability for data to the teams or departments that have the most knowledge and expertise about that data.
• Each domain acts as its own data "product team" responsible for managing and curating the data that is relevant to their specific operations or functions.
• Promotes data democratization and foster a more agile and scalable data infrastructure within theorganization.